1.3 surface according to DIN EN ISO 13918:2008
1.7 assambly tightening torques for threaded studs
1.8 strength of weld stud connections
Technical information
ARNHOLD welding studs are manufactured on modern machines using the cold heading process for highest product quality. All welding studs are subject to continuous quality monitoring for best welding results.
1.1 Materials
Unless otherwise specified, according to the standard DIN EN ISO 13918 "Studs and ceramic rings for arc stud welding".
- Steel
strength class 4.8 (suitable for welding) ISO 891-1 similar to S235 ISO 891-1 Re ≥340N/mm2 - Rust and acid resistant steel A2-50
DIN EN ISO 3506-1 Strength Rm ≥500 N/mm2 , Re≥210N/mm2 - Rust and acid resistant steel A5-50 DIN EN ISO 3506-1
- Aluminum AlMg3 Rm ≥ 100N/mm2
- Brass CuZn 37 Rm≥370N/mm2
- other materials on request
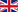
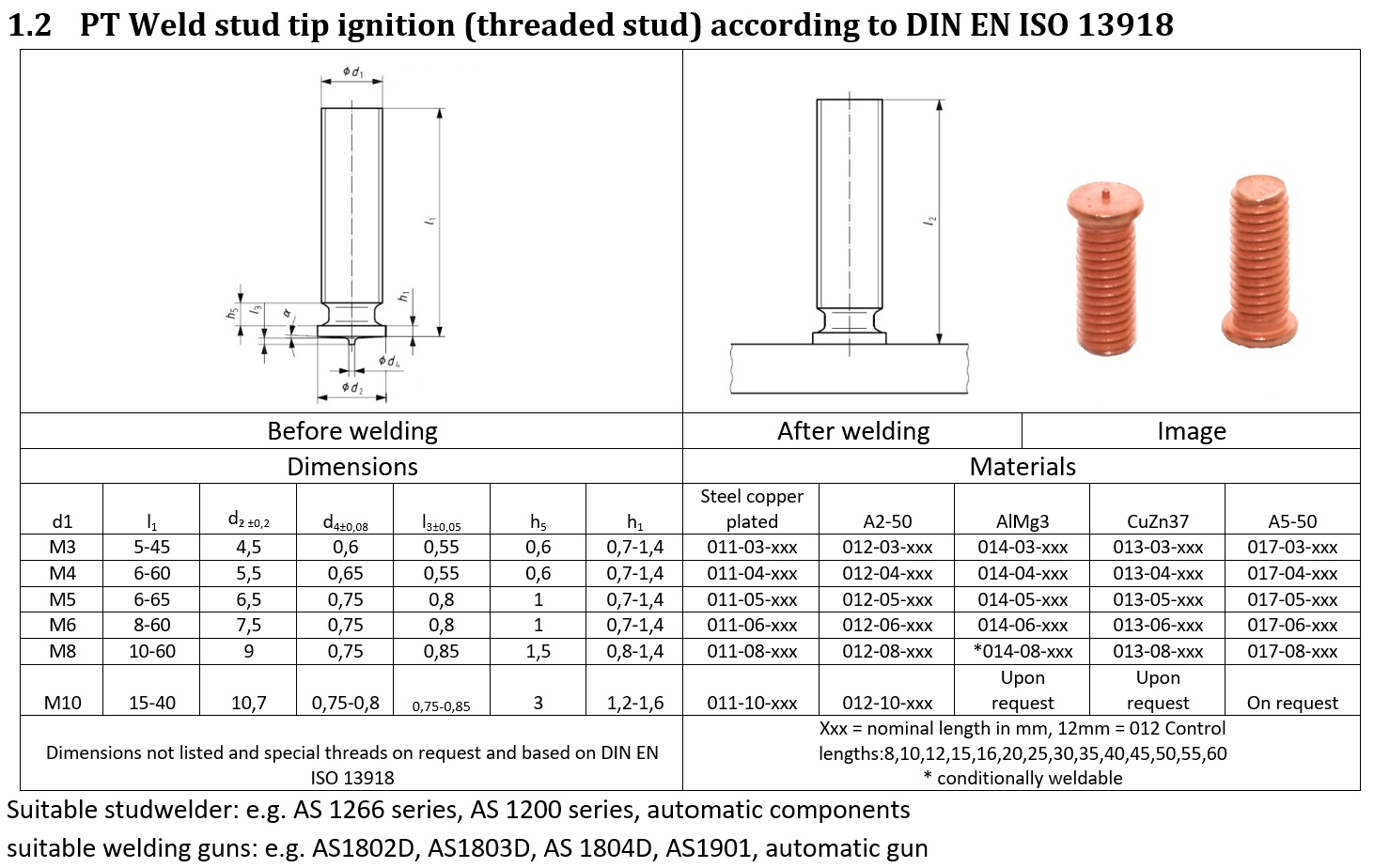
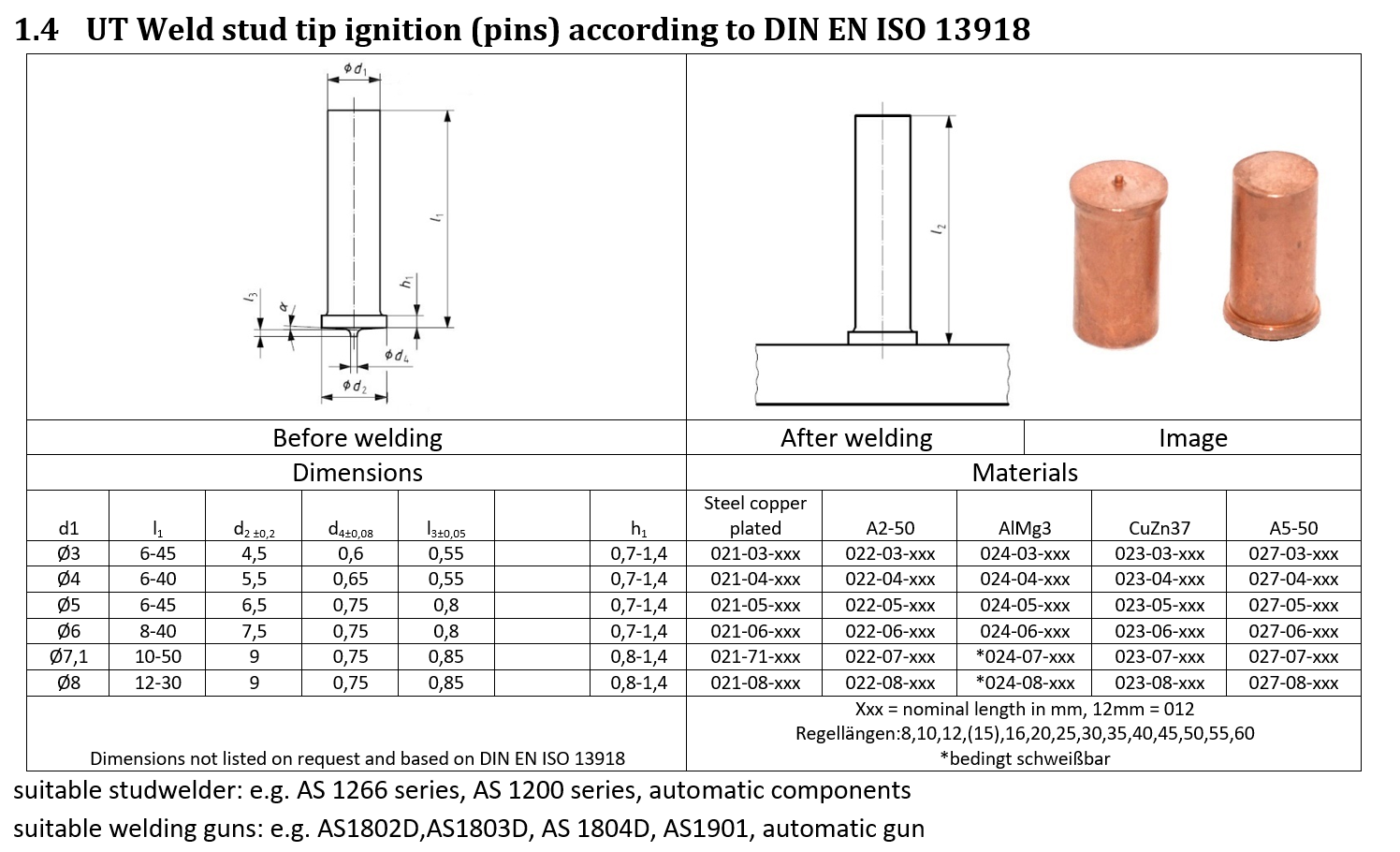
1.2 Dimensions
The dimensions [in mm ]of the studs are described in the tables. All standardized welding studs comply with DIN EN ISO 13918:2008. Non-standardized elements are manufactured in accordance with the standard. Drawing parts on request.
The external threads are usually cold rolled and correspond to tolerance position 6g. The work hardening results in excellent pull-out values in the thread area.
1.3 surface according to DIN EN ISO 13918:2008
Steel bolts are usually provided with a copper coating. This corresponds to C1E (4-8um) unless otherwise specified.
Galvanizing, tin plating, nickel plating and other surfaces are possible on request.
1.4 stud flange
The stud flange serves to increase the welding area, and has positive properties for the arc. It also ensures optimum feedability. An out-of-roundness of the flange within the tolerances is process-related and normal.
For special applications with limited strength requirements, studs with mini-flanges are also manufactured. Please inquire.
1.5 Ignition Tip
An accurately formed ignition tip is crucial for a reliable process. The tolerances are very tight. Nevertheless, for optimum welding results, they should always process all delivery batches separately.
1.6 Usage
Unless otherwise ordered, the welding studs are supplied for use in a manual feeder. Optically sorted goods for highest demands on request.
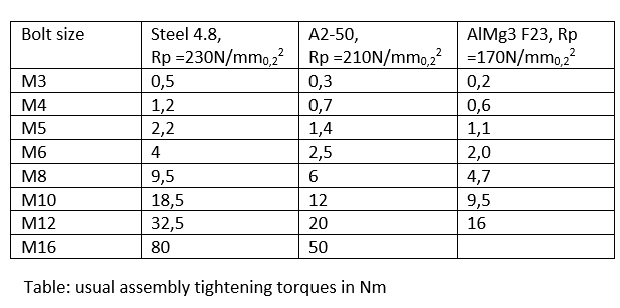
1.7 Assembly tightening torques for threaded studs
The following table shows the minimum tensile force and the minimum torque of a welded joint, without permanent deformation of the workpeace. The requierment is a sufficient thickness of the workpiece material.
The values are valid for threaded studs with standard thread without surface protection and without thread lubrication. Over the entire bolt length, at least the stress cross section must be present (no RD studs). The values apply at the specified yield strengths.The specified values are a recommendation under specified conditions and must be adapted to the actual application.
1.8 Strengths of weld stud connections
Generally, a professional welding assumes that the connection does not fail in the welding. Accordingly, the deformation or fracture occurs in the stud or in the base material. Deviations from this are weld studs with reduced welding range (e.g. mini-flange studs), or unsuitable material pairings, such as black-white connections to be considered differentiated. In case of doubt, the quality of these connections must be verified by a welding procedure qualification test.
The results of the calculation are a stress limit which is defined by the base material or the bolt material with the applied forces. The decisive factor for strength calculations here is the force (tension in the tension cross-section) and the associated material characteristics with a safety factor.