Shielding gas welding is mostly used as a substitute for ceramic ring welding up to stud diameters of 12mm. The shielding gas protects the fusion from the atmosphere and prevents the absorption of nitrogen, prevents oxidation and avoids pore formation. Furthermore, the shielding gas influences the melting behavior, so that a flatter fusion and higher melting on the stud occur compared to welds with ceramics.
Inert gas welding requires gas quantities of around 10-20 l/min, depending on stud size and welding time.
Our long-proven shielding gas technology enables you to achieve ideal welding results with Arnhold stud welding equipment. Our many years of experience and expert advice on the best way to introduce mass to avoid blowing effects make it possible to achieve high-quality welding results.
All in all, stud welding with shielding gas leads to high-quality and visually attractive welding results.
prozess sequenzes:
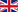
At the beginning, the bolt is placed on the workpiece and is lifted from it. The preflow time of the shielding gas also takes place here. Here, a pilot arc is first generated with a low electric current. After a short " holding time ", the main arc, which melts the materials, is initiated. The shielding gas forms the protective atmosphere. An optimized shielding gas device, such as those of the AS 2901 or 2902, ensure a minimum of arc blowing effects.
All in all the stud is lifted from the workpiece and then plunged into the molten metal of the workpiece during the set welding time. Here, the stud connects with the workpiece. Immediately after the device has been lifted off, the finished weld result is available.
At the end, there is the permanently welded stud. In the graphic, you can find a schematic representation of the welding process.